Former US President Donald Trump has reignited a geopolitical debate by declaring that the United States 'needs' Greenland to ensure its security in the rapidly changing Arctic region. This statement underscores the island's pivotal role in global defence and trade strategies, a status amplified by climate change and international competition.
The Strategic Prize: Location and Resources
Greenland's immense value lies first in its geography. More than 80% of the world's largest island lies above the Arctic Circle, positioning it as a sentinel guarding the North Atlantic approaches to North America. This strategic importance was recognised as far back as World War II, when the US occupied it to prevent a Nazi takeover.
Today, the melting Arctic ice is opening new sea lanes and access to vast resources, transforming the High North into a zone of renewed rivalry. Beyond location, Greenland is a treasure trove of rare earth minerals, essential components for smartphones, computers, batteries, and future green technology. This places it at the centre of Western efforts to reduce dependence on China, which currently dominates this critical market.
Military Footprints and Sovereign Stances
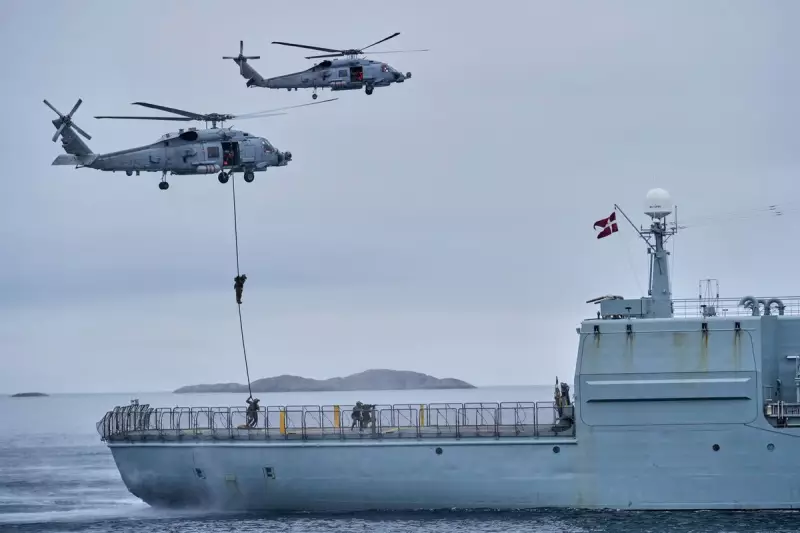
The United States already maintains a significant military presence on the island. The Pituffik Space Base in northwestern Greenland, established under a 1951 treaty with Denmark, is a key node for US and NATO missile warning and space surveillance. Greenland also forms part of the vital GIUK Gap (Greenland, Iceland, United Kingdom), a maritime chokepoint where NATO monitors Russian naval movements.
However, Trump's overtures have been firmly rejected. Greenland is a self-governing territory of Denmark, a longstanding US ally, and both governments have opposed the idea. The island's population of roughly 56,000, predominantly Inuit, insists on determining their own future. In response, Denmark is bolstering its regional presence, announcing a 14.6 billion kroner ($2.3 billion) agreement last year for enhanced surveillance, including new Arctic vessels and drones.
A New Arctic Cold War?
The Arctic's former era of cooperation is under strain. China has labelled itself a 'near-Arctic state' and plans a 'Polar Silk Road', ambitions that drew sharp criticism from former US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo. Meanwhile, Russian President Vladimir Putin has voiced concerns over NATO's Arctic activities, promising a military build-up in response, a stance that has alarmed European leaders since the 2022 invasion of Ukraine.
While development of Greenland's mineral wealth faces hurdles from harsh climates and environmental rules, its strategic significance is undeniable. Trump's comments highlight how this remote island has become a focal point where issues of national security, climate change, and economic competition powerfully converge, setting the stage for continued international focus and diplomatic friction.