Groundbreaking research has revealed that all ChatGPT users can be classified into four entirely new personality types, each with distinct motivations and approaches to artificial intelligence technology. A collaborative study between the University of Oxford and the Berlin University Alliance has identified these categories through detailed analysis of early adopters.
The Four AI Personality Archetypes
In their comprehensive investigation, scientists examined 344 individuals who began using ChatGPT within the first four months of its public release on November 30, 2020. The research team discovered that traditional "one-size-fits-all" approaches to technology adoption completely fail to capture the nuanced relationship users develop with advanced AI systems.
AI Enthusiasts: The Socially Engaged Pioneers
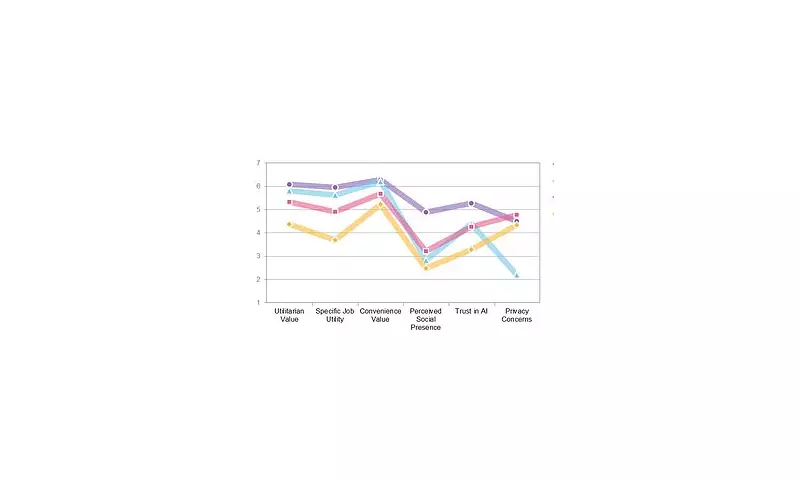
Representing 25.6 percent of participants, AI enthusiasts constitute the most technologically sophisticated user group. These individuals demonstrate high engagement levels while seeking both productivity enhancements and social benefits from contemporary AI systems. Remarkably, this group uniquely perceives a "social presence" when interacting with chatbots, often treating AI tools as genuine conversational partners capable of fulfilling social connection needs.
Dr Christoph Gerling from the Humboldt Institute for Internet and Society, the study's lead author, explains: "Using AI feels intuitive, but mastering it requires exploration, prompting skills and learning through experimentation. This makes the 'task-technology fit' more dependent on the individual than ever before."
Naïve Pragmatists: Results-Oriented Utility Seekers
Comprising 20.6 percent of surveyed users, naïve pragmatists prioritise convenience and tangible outcomes above all other considerations. These utility-driven individuals strongly believe in AI's practical and job-specific benefits while showing less interest in social dimensions than their enthusiast counterparts. Researchers note this group tends to prioritise AI advantages over potential privacy concerns, potentially exposing themselves to greater technological risks.
Cautious Adopters: The Vigilant Majority
As the largest category at 35.5 percent, cautious adopters approach AI with curiosity tempered by vigilance. These pragmatic users constantly evaluate functional benefits against potential drawbacks, demonstrating significantly greater privacy concerns than both AI enthusiasts and naïve pragmatists. Their balanced perspective represents the most common approach among early ChatGPT users.
Reserved Explorers: The Tentative Sceptics
Making up 18.3 percent of participants, reserved explorers represent the most apprehensive user segment. These sceptical individuals are merely "dipping a toe" into AI waters while remaining unconvinced about the technology's personal benefits. Unlike other groups, reserved explorers struggle to identify ChatGPT's advantages while maintaining substantial privacy concerns.
Surprising Findings and Implications
The research revealed a particularly striking discovery: despite three of the four user groups expressing serious privacy concerns about ChatGPT, all continued using the AI chatbot regardless. This paradox suggests that perceived utility often outweighs privacy apprehensions in practical technology adoption.
Based on these observations, researchers caution against excessive anthropomorphisation of AI systems. They warn that privacy-conscious users might begin blaming AI itself for potential violations rather than the companies behind the technology, potentially eroding trust more rapidly than anticipated.
The study fundamentally challenges previous assumptions about technology adoption, demonstrating that AI interaction patterns vary dramatically according to individual personality characteristics rather than following predictable, uniform trajectories.